Uncategorized
How Do Mushrooms Develop Psychedelic Properties?
Psychedelic mushrooms have fascinated humans for centuries. At Newphoria, we’re diving into the intriguing world of fungi to explore how mushrooms become psychedelic.
This blog post will uncover the science behind these mind-altering organisms, from their chemical makeup to the environmental factors that influence their potency. We’ll also examine the evolutionary perspective on why these fungi developed their unique properties.
What Makes Mushrooms Psychedelic?
The Chemical Powerhouses: Psilocybin and Psilocin
Psychedelic mushrooms contain a group of chemical compounds that produce mind-altering effects. Psilocybin and psilocin stand out as the primary active ingredients. These natural substances occur in over 200 mushroom species, predominantly within the Psilocybe genus.
Psilocybin acts as the main psychoactive compound in magic mushrooms. However, psilocybin itself doesn’t cause psychedelic effects directly. Upon ingestion, the human body rapidly converts psilocybin to psilocin. Psilocin then interacts with the brain’s serotonin receptors (particularly the 5-HT2A receptor), which leads to altered perceptions and consciousness.

A 2020 study in the Journal of Psychopharmacology revealed psilocybin’s potential therapeutic benefits. The research found that 80% of cancer patients experienced significant and long-lasting reductions in anxiety and depression symptoms four years after receiving psilocybin treatment.
The Mushroom’s Chemical Factory
The biosynthesis of psilocybin in mushrooms involves a fascinating process. It begins with the amino acid tryptophan, which undergoes a series of enzymatic reactions. Four key enzymes (PsiD, PsiK, PsiM, and PsiH) work in concert to transform tryptophan into psilocybin through several intermediate compounds.
Psilocybin concentration varies greatly between different mushroom species and even within the same species. For instance, Psilocybe cubensis typically contains between 0.14% to 0.42% psilocybin by dry weight. In contrast, the potent Psilocybe azurescens can contain up to 1.78% (nearly four times as much).
Environmental Influences on Potency
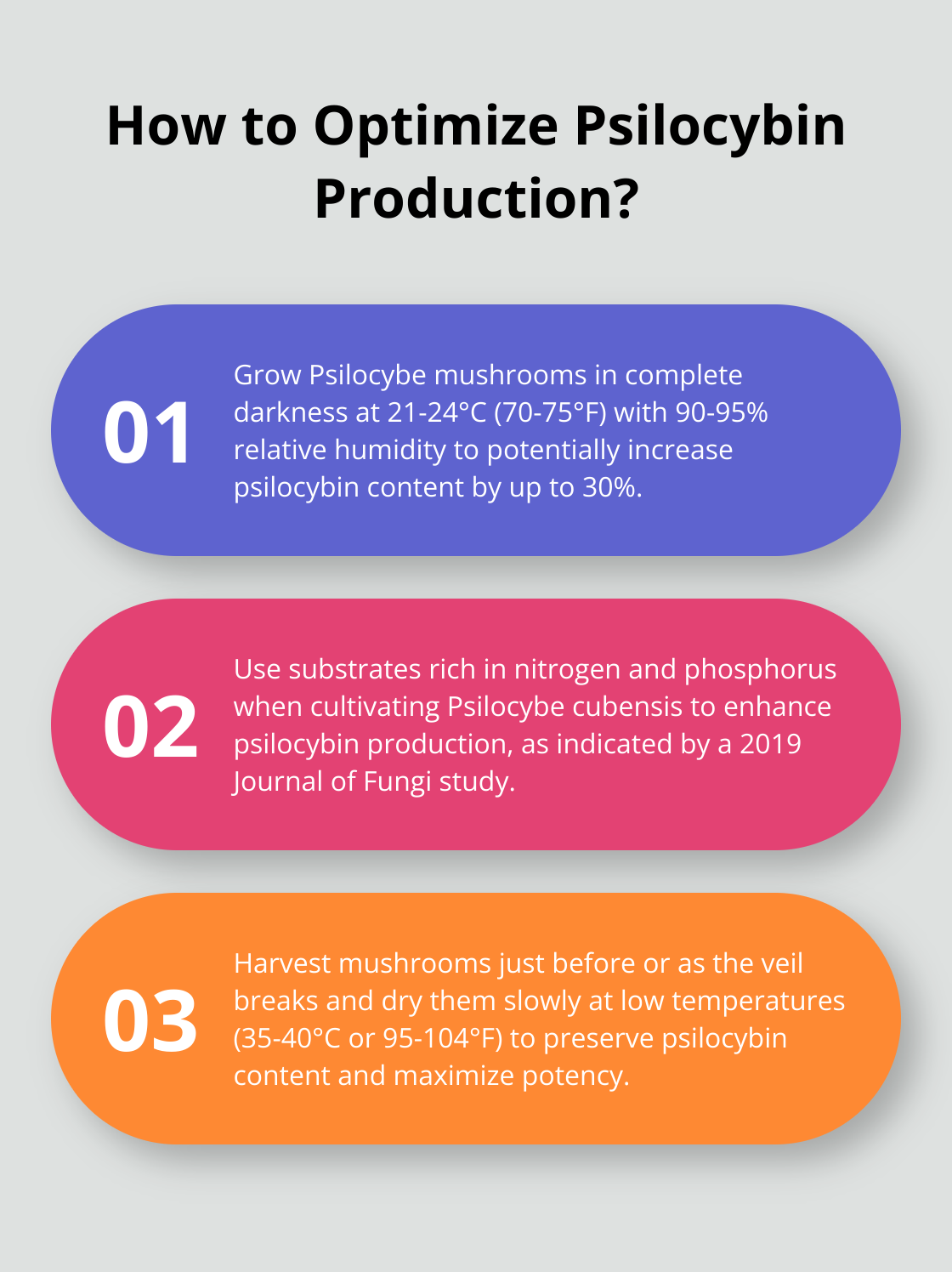
Genetics alone don’t determine the potency of psychedelic mushrooms. Environmental factors play a crucial role in psilocybin production. A 2017 study in Fungal Biology found that light exposure during growth significantly affected psilocybin content. Mushrooms grown in complete darkness showed higher psilocybin levels compared to those grown under light-dark cycles.
Temperature and humidity also impact psilocybin production. Most Psilocybe species thrive in temperatures between 21-24°C (70-75°F) and relative humidity around 90-95%. Maintaining these conditions can potentially increase psilocybin content by up to 30%.
Strain Variations and Potency
Different strains of psychedelic mushrooms exhibit varying levels of potency. Popular strains like Penis Envy and Golden Teacher have gained reputations for their consistent and potent effects. The Penis Envy strain, in particular, has been the subject of anecdotal reports regarding its potency.
Genetic factors contribute to these variations in potency. Researchers continue to study the genetic makeup of different mushroom strains to understand how specific genes influence psilocybin production. This knowledge could lead to the development of new strains with tailored potency levels for various applications (medicinal or recreational).
As we explore the fascinating world of psychedelic mushrooms, it becomes clear that their potency results from a complex interplay of genetics, environment, and biochemistry. Understanding these factors not only satisfies scientific curiosity but also paves the way for more effective and targeted applications of these remarkable fungi. In the next section, we’ll examine the evolutionary perspective on why mushrooms developed these unique psychoactive properties.
What Shapes Mushroom Potency?
The Influence of Light and Temperature
Light exposure impacts psilocybin production in mushrooms significantly. A journey with psychedelic mushrooms reveals their historical relevance, biology, cultivation, medicinal uses, and biotechnological potential. This finding suggests that cultivators who want maximum potency should consider various factors during the growth phase.

Temperature also plays a vital role. Most Psilocybe species thrive in temperatures between 21-24°C (70-75°F). Maintaining this optimal temperature range can influence psilocybin content. However, some strains, like Psilocybe azurescens, prefer cooler temperatures and can produce higher psilocybin levels in these conditions.
The Role of Humidity and Substrate
Humidity is another critical factor. Psilocybe mushrooms generally prefer high humidity levels (around 90-95% relative humidity). Proper moisture management not only promotes healthy growth but also influences psilocybin production.
The substrate composition affects potency as well. A 2019 Journal of Fungi study found that substrates rich in nitrogen and phosphorus led to increased psilocybin production in Psilocybe cubensis. This suggests that carefully formulated growing mediums could enhance the potency of cultivated mushrooms.
Genetic Variations and Strain Selection
While environmental factors matter, genetics still play a significant role in determining mushroom potency. Different strains of Psilocybe cubensis can vary widely in their psilocybin content. Penis envy mushrooms, a type of magic mushroom, may have potential benefits but also come with safety and legality concerns.
Ongoing research in genetic sequencing sheds light on the genes responsible for psilocybin production. This knowledge could lead to the development of new strains tailored for specific applications (whether medicinal or recreational).
Harvesting and Drying Techniques
The timing of harvest can significantly impact potency. Many cultivators believe that harvesting just before or as the veil breaks results in the highest psilocybin concentration. However, this theory lacks solid scientific backing and requires further research.
Drying techniques also influence final potency. Slow drying at low temperatures (around 35-40°C or 95-104°F) often preserves psilocybin content. Rapid drying at high temperatures can potentially degrade some of the psychoactive compounds.
Understanding these factors proves important for both cultivators and consumers. For those who seek the most potent experience, choosing the right strain, grown under optimal conditions, and properly harvested and dried, can make a significant difference. However, it’s essential to approach high-potency mushrooms with caution, as their effects can be intense and potentially overwhelming for inexperienced users.
As we explore the factors that shape mushroom potency, we can’t help but wonder: why did these fungi develop such unique properties in the first place? In the next section, we’ll examine the evolutionary perspective on psychedelic mushrooms and their fascinating relationship with humans and other animals.
Why Did Mushrooms Evolve Psychedelic Properties?
Psychedelic mushrooms have captivated humans for millennia, but their existence raises a fascinating question: Why did these fungi evolve to produce mind-altering compounds? The evolutionary story behind these remarkable organisms reveals intriguing theories and potential explanations.
A Defense Mechanism Against Predators
One leading theory suggests that psilocybin evolved as a defense mechanism. Insects, particularly fungus-eating ones, pose a significant threat to mushrooms. A study published in Evolution Letters in 2018 by researchers at The Ohio State University found that psilocybin might deter these predators.

The study revealed that psilocybin targets neurotransmitter receptors in insects, potentially altering their behavior or appetite. This chemical defense could give psychedelic mushrooms an evolutionary edge, allowing them to thrive in insect-rich environments like animal dung and decaying wood.
Facilitating Spore Dispersal
Another intriguing hypothesis proposes that psilocybin might aid in spore dispersal. Some researchers speculate that animals consuming these mushrooms might exhibit altered behavior, potentially traveling further and dispersing spores over a wider area.
While this theory lacks conclusive evidence, it aligns with observations of certain animals deliberately seeking out psychoactive plants and fungi. For instance, reindeer in Siberia have been observed consuming Amanita muscaria mushrooms, exhibiting unusual behavior afterward.
Co-evolution with Humans
The relationship between psychedelic mushrooms and humans adds another layer to their evolutionary story. Some anthropologists argue that early human use of these fungi might have influenced our cognitive and cultural evolution.
Terence McKenna, an ethnobotanist and mystic, proposed the controversial Stoned Ape theory in his 1992 book “Food of the Gods”. He suggested that psilocybin consumption by early hominids could have catalyzed the rapid expansion of the human brain and the development of language and culture.
While this theory remains speculative, it highlights the long-standing relationship between humans and psychedelic fungi. This interaction could have influenced the survival and spread of certain mushroom species, indirectly shaping their evolution.
Ecological Advantages
The presence of psilocybin in mushrooms may offer ecological advantages beyond defense and spore dispersal. Some researchers hypothesize that these compounds could enhance the fungi’s ability to compete for resources or adapt to changing environmental conditions.
For example, psilocybin might influence soil microbiota in ways that benefit the mushroom’s growth or nutrient absorption. This potential ecological role remains an active area of research, with scientists exploring the complex interactions between psychedelic mushrooms and their environments.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Understanding the evolutionary history of psychedelic mushrooms not only satisfies scientific curiosity but also informs their potential applications. As research into psilocybin’s therapeutic potential continues, insights from evolutionary biology could guide the development of new treatments for mental health conditions.
Scientists are now employing advanced genetic sequencing techniques to unravel the mysteries of psilocybin biosynthesis in different mushroom species. This research may reveal new compounds with unique properties and shed light on the evolutionary pathways that led to the development of psychedelic traits in fungi.
Final Thoughts
The journey of how mushrooms become psychedelic reveals a fascinating tale of evolution, chemistry, and environmental adaptation. From the intricate biosynthesis of psilocybin to the complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors, these fungi have developed unique properties that continue to captivate researchers and enthusiasts. Understanding the science behind psychedelic mushrooms proves essential for their safe and responsible use.
The evolutionary perspective on why mushrooms developed psychedelic properties offers intriguing insights into the ecological roles of these compounds. Scientists continue to explore the genetic basis of psilocybin production, which could lead to the development of new strains with tailored properties for therapeutic applications. Ongoing studies into the ecological functions of psilocybin may reveal new insights into fungal biology and ecosystem dynamics.
As interest in psychedelic mushrooms grows, it’s important to approach their use with respect and caution. For those interested in exploring these fascinating fungi, Newphoria offers a range of psychedelic products, including renowned mushroom strains. The story of how mushrooms become psychedelic continues to unfold, promising to uncover more secrets about these enigmatic organisms.

