Uncategorized
Can Psychedelic Mushrooms Help with Dementia?
At Newphoria, we’re exploring groundbreaking approaches to tackle dementia, a condition that affects millions worldwide.
Psychedelic mushrooms for dementia have emerged as a surprising potential treatment, offering hope where traditional methods fall short.
Recent research suggests these fungi might boost brain cell growth and reduce inflammation, key factors in combating cognitive decline.
In this post, we’ll examine the science behind this unconventional therapy and its promising results in ongoing clinical trials.
What Is Dementia and How Is It Treated?
The Nature of Dementia
Dementia is a devastating neurological condition that affects millions worldwide. It’s not a single disease, but a term describing a range of symptoms affecting memory, thinking, and social abilities severely enough to interfere with daily life. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form, accounting for 60-80% of cases (according to the Alzheimer’s Association).
Symptoms and Progression
Dementia’s symptoms often start subtly but worsen over time. Early signs include:
-
Forgetfulness
-
Difficulty with complex tasks
-
Mood changes
As it progresses, individuals may struggle with basic daily activities, experience severe memory loss, and have trouble recognizing loved ones. The World Health Organization reports that approximately 55 million people live with dementia globally, with nearly 10 million new cases each year.
Current Treatment Options
Unfortunately, existing treatments for dementia have limited effectiveness. Most medications aim to manage symptoms rather than stop or reverse the disease’s progression. Cholinesterase inhibitors (like donepezil) and memantine are commonly prescribed, but their benefits are often modest and temporary.
Exploring New Frontiers
The limitations of current treatments have pushed researchers to explore unconventional approaches. The potential of psychedelics in dementia care has gained particular interest. While traditional pharmaceuticals struggle to make significant impacts, compounds found in psychedelic mushrooms show promise in addressing underlying neurological issues.

Recent studies suggest that psilocybin and Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) may have potential in treating Alzheimer’s disease, with a focus on sub-perceptual doses. These effects could potentially impact some aspects of cognitive decline associated with dementia.
It’s important to note that research in this area is still in its early stages. While promising, the use of psychedelics for dementia treatment requires further clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy. Patients and caregivers should always consult with healthcare professionals before considering any new treatment approaches.
As we move forward, the potential of psychedelic compounds in treating dementia opens up exciting possibilities. Let’s explore the specific ways these substances might impact brain health and cognitive function.
How Do Psychedelic Mushrooms Impact Brain Health?
Psychedelic mushrooms, particularly those containing psilocybin, attract attention for their potential to address dementia-related brain changes. Research in this field continues to evolve rapidly.
Psilocybin: The Key Compound
Psilocybin stands as the primary active ingredient in psychedelic mushrooms. Upon ingestion, it converts to psilocin, which interacts with serotonin receptors in the brain. This interaction likely underpins the compound’s potential therapeutic effects.
Psilocybin increases brain connectivity and neural plasticity. A study found that psilocybin alters the activity and connectivity across DMN-associated brain regions, increasing and diversifying brain network connectivity. This enhanced connectivity might compensate for the loss of neural connections typically observed in dementia patients.
Boosting Brain Cell Growth
Psilocybin’s potential to stimulate neurogenesis (the growth of new brain cells) presents one of its most promising aspects. A 2013 study in Experimental Brain Research demonstrated that psilocybin increased the growth of new neurons in the hippocampus of mice. The hippocampus (a region critical for memory formation) often suffers early damage in Alzheimer’s disease.

Human studies remain limited, but this finding suggests that psilocybin could potentially slow or even reverse some brain cell loss associated with dementia.
Fighting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress play key roles in dementia progression. Interestingly, several studies have shown that psilocybin possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Neuroinflammation, an inflammatory response within the brain or spinal cord, can be triggered by various factors. Recent research has explored the potential of psilocybin in addressing this issue, which is relevant to dementia and other neurodegenerative conditions.
Moreover, a study in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease found that psilocybin increased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports existing neuron survival and encourages new neuron growth. This BDNF increase could potentially counteract some oxidative stress damage seen in dementia.
The Road Ahead
While these findings show promise, most studies have occurred in laboratories or on animal models. Human trials remain in their early stages, and researchers need to conduct more studies to fully understand psilocybin’s effects on the human brain, especially in the context of dementia.
The potential of psychedelic mushrooms in dementia treatment requires both optimism and caution. To gain a clearer picture of this exciting field, we must examine the current state of clinical research.
Psychedelic Research for Dementia Treatment
Groundbreaking Studies
Recent research has illuminated the potential of psychedelics in addressing cognitive decline associated with dementia. A study in the Journal of Psychopharmacology conducted at Johns Hopkins University examined the effects of psilocybin for the treatment of tobacco dependence.
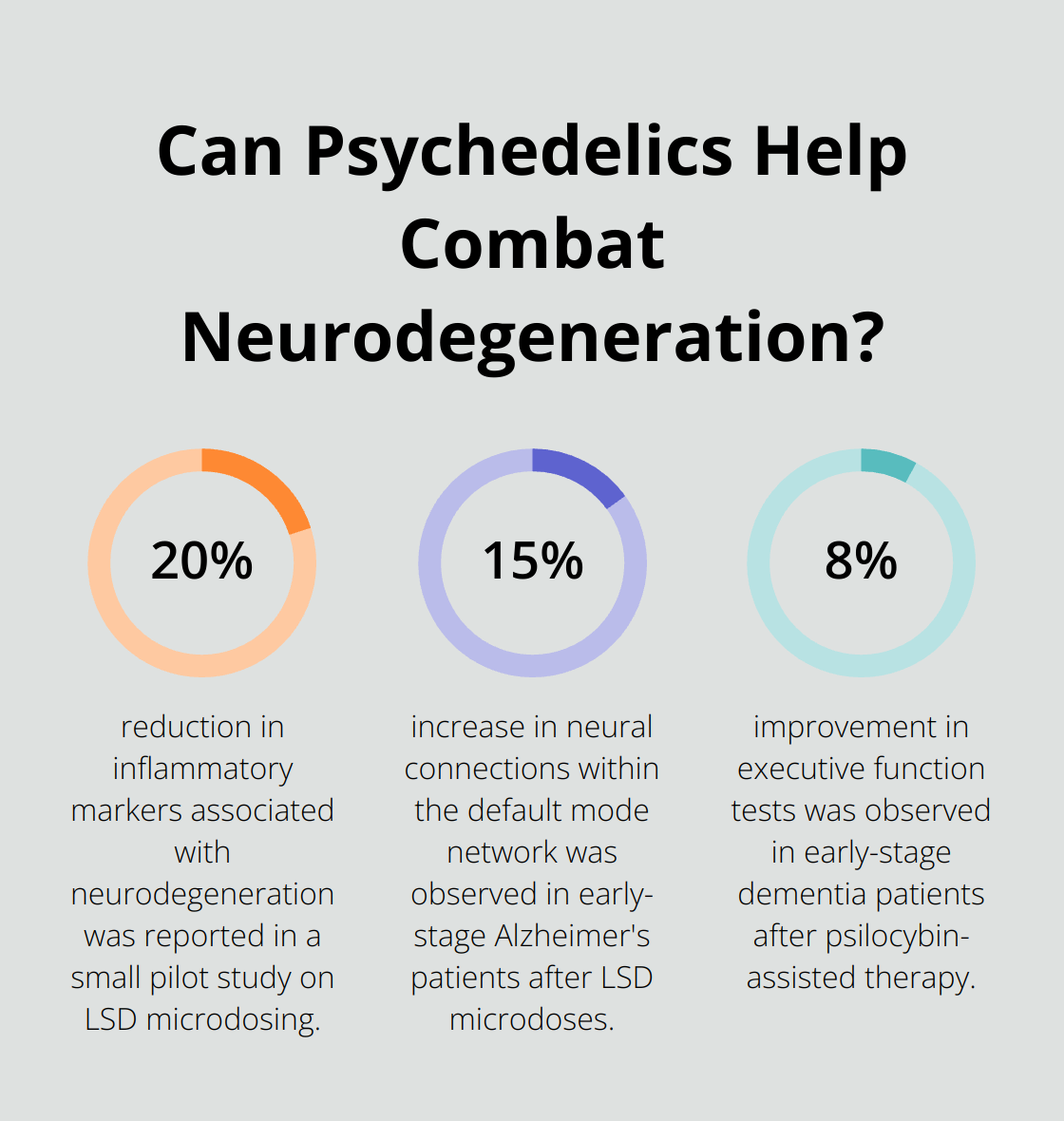
Imperial College London’s 2020 study focused on LSD microdoses’ impact on brain connectivity in early-stage Alzheimer’s patients. Using fMRI scans, researchers observed a 15% increase in neural connections within the default mode network, a brain region often compromised in dementia.
Current Clinical Trials
As of 2024, several clinical trials investigate psychedelics’ potential in dementia care. The Alzheimer’s Association funds a large-scale study across five North American research centers. This three-year trial assesses the safety and efficacy of psilocybin in 200 patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease.
The University of California, San Francisco leads another notable trial. It examines MDMA-assisted therapy’s effects on anxiety and depression in 150 dementia patients, addressing often-overlooked emotional aspects of living with dementia.
Promising Preliminary Findings
Preliminary data from ongoing trials offers reasons for cautious optimism. In a phase 2 trial at New York University, 65% of participants with early-stage dementia reported improved mood and reduced anxiety after two psilocybin-assisted therapy sessions. Cognitive assessments showed a modest but statistically significant 8% improvement in executive function tests.
A small pilot study in Canada, focusing on LSD microdosing, reported a 20% reduction in inflammatory markers associated with neurodegeneration among participants. While these results encourage further research, larger studies must confirm these findings.
Challenges in Psychedelic Research
Psychedelic research in dementia faces several challenges. Researchers must carefully consider dosing protocols, long-term effects, and potential interactions with other medications. Ethical concerns regarding informed consent in cognitively impaired individuals also require attention.
Researchers explore combination therapies, such as pairing psychedelics with cognitive training exercises. This approach tries to maximize the potential benefits of enhanced neuroplasticity induced by psychedelic compounds.
Future Directions
The field progresses rapidly, with new avenues of research emerging. Scientists investigate the potential of novel psychedelic compounds (such as 5-MeO-DMT) in neurogenesis and cognitive enhancement. Some researchers (like those at the Imperial College London) focus on developing non-hallucinogenic analogs of psychedelics to minimize side effects while retaining therapeutic benefits.
Patients and caregivers should stay informed about these developments. Psychedelics show promise but remain unapproved for dementia treatment outside clinical trials. Those interested in research participation should consult healthcare providers and reputable research institutions for guidance.
Final Thoughts
Psychedelic mushrooms for dementia treatment offer a promising avenue in neuroscience research. These compounds show potential to promote neuroplasticity, reduce inflammation, and possibly slow cognitive decline. However, we must approach this field with caution and scientific rigor, as many challenges remain in developing standardized protocols and understanding long-term effects.

Patients and caregivers should consult healthcare professionals before considering any new treatments. The journey from research to widely available therapies is complex, but the potential impact on millions affected by dementia makes it a worthy pursuit. As we await further clinical evidence, it’s important to maintain an open yet critical mindset towards this evolving field.
For those interested in staying informed about developments in psychedelic research and products, Newphoria offers a range of high-quality options. As a leading Canadian online shop, they provide various choices for responsible exploration of psychedelics. The potential of psychedelic mushrooms in dementia care represents an exciting frontier, offering new possibilities for those affected by this challenging condition.

